Everything You Need to Know About Thickening Agent and How AI Eat This Can Help
Thickening agent is a broad category of food additives used to modify the texture and consistency of countless food products. For consumers with dietary restrictions, food allergies, or specific health concerns, identifying thickening agent in ingredient lists can be challenging and time-consuming. The AI Eat This app revolutionizes this process by instantly scanning ingredient lists in any language, helping you make informed decisions about the foods you consume.
Understanding what thickening agent encompasses and where it appears in your diet is crucial for maintaining your health goals. Whether you're managing allergies, following specific dietary protocols, or simply want to avoid certain food additives, knowing how to identify thickening agent can significantly impact your food choices.
What Is Thickening Agent and Where Is It Used?
Thickening agent refers to various substances added to food products to increase viscosity, improve texture, or create desired consistency without substantially changing other properties. These food additives play essential roles in modern food manufacturing, helping create the smooth textures we expect in sauces, soups, and processed foods.
Common types of thickening agent include natural options like cornstarch, arrowroot, and guar gum, as well as synthetic alternatives such as modified food starch and various gums. Each type serves specific purposes and may be identified by different names or E-numbers on ingredient labels.
Common Foods Containing Thickening Agent
Thickening agent appears in numerous everyday food products, often in unexpected places. Understanding where to look for these additives helps consumers make better-informed choices about their dietary intake.
- Soups, sauces, and gravies
- Dairy products like yogurt and ice cream
- Salad dressings and condiments
- Baked goods and desserts
- Processed meats and ready meals
- Beverages and smoothies
- Gluten-free products
Is Thickening Agent Safe? What Does the Research Say?
The safety of thickening agent varies depending on the specific substance and individual tolerance levels. Most commonly used thickening agents have received approval from major regulatory bodies, including the FDA, EFSA, and WHO.
Regulatory Approvals and Guidelines
Regulatory agencies have established acceptable daily intake levels for various thickening agents based on extensive safety studies. Natural thickening agents like guar gum and xanthan gum are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA. However, some individuals may experience digestive discomfort when consuming large quantities of certain thickening agents.
The CDC monitors food additive safety and provides guidance on potential health concerns. Most thickening agents pose minimal risk to the general population when consumed within normal dietary ranges.
Risks for Specific Groups
While thickening agent is generally safe, certain individuals may need to exercise caution. People with specific allergies or intolerances may react to particular thickening agents, especially those derived from common allergens like wheat or corn.
Those following strict dietary restrictions, such as ketogenic or paleo diets, may choose to avoid certain thickening agents that don't align with their nutritional goals. Additionally, some individuals experience digestive sensitivity to high-fiber thickening agents.
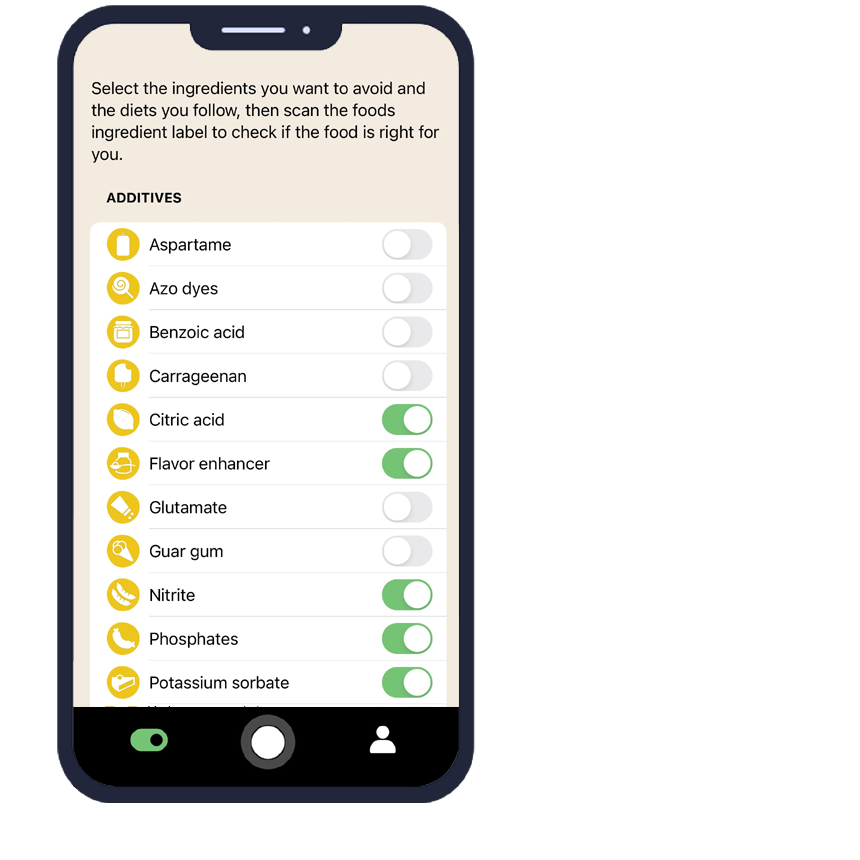
How Does AI Eat This Help You Avoid Thickening Agent?
The AI Eat This application transforms how consumers identify thickening agent in food products. Using advanced artificial intelligence, the app scans ingredient lists through your smartphone camera, instantly recognizing thickening agents regardless of the language on the packaging.
Users can set personalized filters based on their specific dietary restrictions, allergies, or preferences. When scanning products, the app immediately alerts you if thickening agent is present, along with detailed information about the specific type detected.
The app's comprehensive database includes various names and E-numbers for thickening agents, ensuring nothing slips through undetected. This feature proves invaluable for people managing multiple dietary restrictions or those unfamiliar with technical ingredient names.
Who Should Avoid Thickening Agent?
Several groups of people may benefit from avoiding or limiting thickening agent consumption. Individuals with diagnosed allergies to specific thickening agents should completely avoid products containing these substances.
People following elimination diets or those with digestive sensitivities may choose to avoid certain thickening agents that commonly trigger symptoms. Some thickening agents can cause bloating, gas, or other gastrointestinal discomfort in sensitive individuals.
Those adhering to specific dietary protocols, such as whole food diets or clean eating approaches, may prefer to minimize consumption of processed foods containing thickening agents. The NIH provides resources for understanding how food additives fit into various dietary approaches.
Tips for a Thickening Agent-Free Diet
Successfully avoiding thickening agent requires strategic planning and careful label reading. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods that naturally don't require texture modification.
When shopping, prioritize fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. These foods provide nutrition without added thickening agents while supporting overall health goals.
- Read ingredient labels carefully, looking for both common names and E-numbers
- Choose homemade versions of sauces, soups, and dressings when possible
- Use natural thickening alternatives like pureed vegetables or reduction techniques
- Utilize the AI Eat This app for quick ingredient scanning while shopping
- Research restaurants' ingredient lists before dining out
Meal planning becomes easier when you understand which products typically contain thickening agent. Preparing meals from scratch gives you complete control over ingredients while often providing better nutritional value.
Conclusion
Understanding thickening agent and its presence in food products empowers consumers to make informed dietary choices aligned with their health goals and restrictions. While most thickening agents are safe for general consumption, individuals with specific needs benefit from careful monitoring and avoidance strategies.
The AI Eat This app simplifies the process of identifying thickening agent in food products, making dietary management more accessible and reliable. With instant ingredient scanning and personalized filtering capabilities, maintaining your preferred diet becomes significantly easier.
Take control of your dietary choices today. Download AI Eat This for free testing and experience how technology can support your health journey by helping you identify and avoid unwanted thickening agent in your food!
70 filters
With over 70 filters, you can easily avoid certain ingredients and follow your dietary preference.

Paleo
Pescetarian

Ultra-processed food

Vegan