Everything You Need to Know About Sesame and How AI Eat This Can Help You Avoid It
Sesame is one of the most common food allergens worldwide, yet it often goes unnoticed in ingredient lists until it's too late. For millions of people with Sesame allergies or dietary restrictions, identifying this ingredient in packaged foods can be a daily challenge. The AI Eat This mobile app revolutionizes how consumers detect Sesame and other unwanted ingredients by scanning food labels in any language, making grocery shopping safer and more convenient for those with specific dietary needs.
What Is Sesame and Where Is It Used?
Sesame refers to seeds from the Sesamum indicum plant, commonly used as both a flavoring agent and nutritional ingredient in countless food products. These small, oil-rich seeds have been cultivated for thousands of years and are prized for their nutty flavor and high protein content. In the food industry, Sesame appears in various forms including whole seeds, oil, paste (tahini), and flour.
The versatility of Sesame makes it a popular food additive across many cuisines and processed foods. You'll commonly find it in bread products, crackers, energy bars, salad dressings, and Asian cuisine. Many consumers don't realize that Sesame can also appear under alternative names on ingredient labels, making identification challenging without proper tools.
Common Foods Containing Sesame
Sesame appears in numerous everyday products, often in unexpected places:
- Bakery items like hamburger buns, bagels, and crackers
- Snack foods including pretzels, chips, and trail mixes
- Condiments such as tahini, hummus, and certain salad dressings
- Asian foods like sushi, stir-fry sauces, and noodle dishes
- Processed meats and vegetarian protein products
- Cosmetics and personal care products (non-food applications)
Is Sesame Safe? What Does the Research Say?
For most people, Sesame is completely safe and provides valuable nutrients including healthy fats, protein, and minerals. The FDA, EFSA, and WHO all recognize Sesame as safe for general consumption. However, regulatory agencies worldwide have increasingly recognized Sesame as a major allergen requiring special labeling considerations.
Regulatory Approvals and Guidelines
In 2021, the FDA officially recognized Sesame as the ninth major food allergen in the United States, requiring clear labeling on packaged foods. This regulatory change acknowledges the significant health risks Sesame poses to allergic individuals. The European Food Safety Authority has similarly classified Sesame as a priority allergen requiring mandatory declaration on food labels.
These regulatory frameworks ensure that food manufacturers must clearly identify Sesame-containing ingredients, helping consumers make informed choices about their dietary restrictions.
Risks for Specific Groups
While generally safe, Sesame can trigger severe allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Sesame allergy affects approximately 0.1-0.2% of the population, but reactions can range from mild symptoms to life-threatening anaphylaxis. Unlike some food allergies that children may outgrow, Sesame allergy typically persists into adulthood.
Cross-contamination during food processing also poses risks, as trace amounts of Sesame can trigger reactions in highly sensitive individuals. This makes careful ingredient screening essential for anyone with Sesame-related dietary restrictions.
How AI Eat This Helps You Avoid Sesame
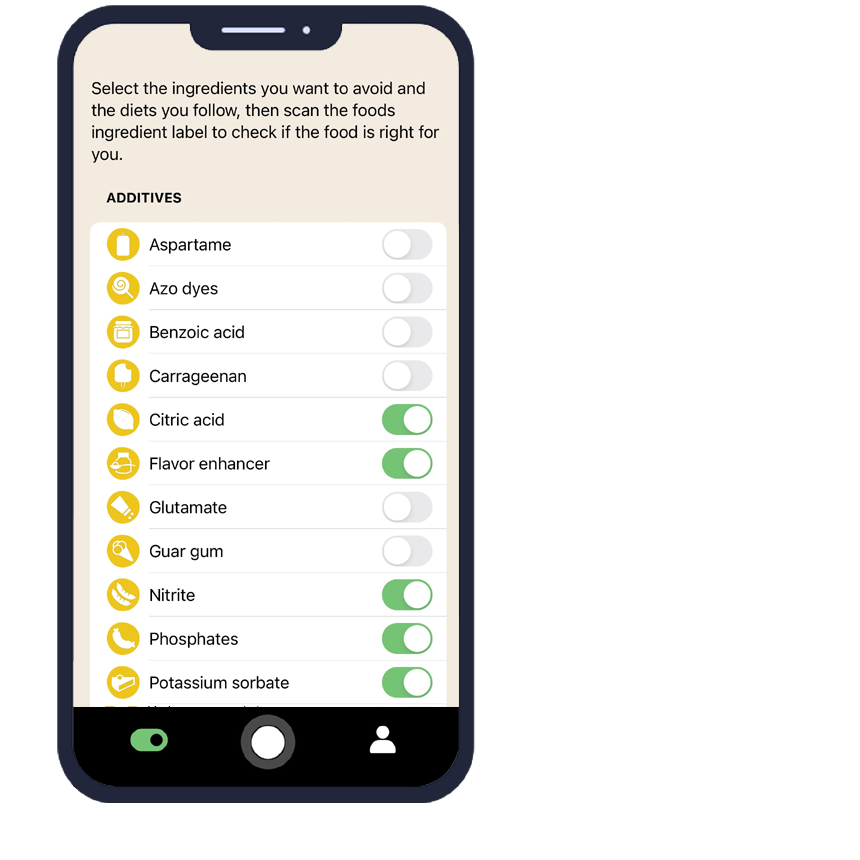
The AI Eat This app transforms how consumers identify Sesame in food products through advanced ingredient scanning technology. Simply point your phone's camera at any food label, and the app instantly analyzes the ingredient list in any language, highlighting Sesame and other unwanted additives.
Users can create personalized dietary profiles that automatically flag Sesame-containing products before purchase. The app's intelligent algorithms recognize various forms of Sesame, including alternative names and chemical codes that might confuse traditional label reading. This technology is particularly valuable for travelers or when shopping for international products with unfamiliar labeling.
The app's database continuously updates with new product information and regulatory changes, ensuring users always have access to the most current Sesame identification capabilities. For families managing multiple dietary restrictions, AI Eat This allows multiple user profiles, making grocery shopping efficient for everyone's needs.
Who Should Avoid Sesame?
Several groups should carefully monitor their Sesame intake or avoid it entirely. Individuals with diagnosed Sesame allergy must completely eliminate all forms of this ingredient from their diet, as even trace amounts can trigger reactions. Parents of children with Sesame allergy face additional challenges, as cross-contamination in school cafeterias and social settings requires constant vigilance.
Some people experience Sesame intolerance, which causes digestive discomfort rather than allergic reactions. While less severe than true allergies, these individuals benefit from identifying and limiting Sesame consumption. Additionally, certain religious or cultural dietary restrictions may require avoiding Sesame-containing products.
Healthcare providers often recommend Sesame avoidance for patients with multiple food allergies, as cross-reactivity between allergens can complicate dietary management.
Tips for a Sesame-Free Diet
Successfully avoiding Sesame requires strategic shopping and meal planning approaches. Always read ingredient labels carefully, as Sesame can appear under various names including "tahini," "sesame oil," or simply as "natural flavoring" in some products.
Focus on whole, unprocessed foods when possible, as fresh fruits, vegetables, and plain meats naturally contain no added Sesame. When dining out, inform restaurant staff about your Sesame allergy and ask about ingredient lists and preparation methods.
Consider these practical strategies:
- Use the AI Eat This app for quick ingredient verification
- Shop at stores with clear allergen labeling policies
- Prepare homemade versions of commonly Sesame-containing foods
- Keep emergency medication accessible if you have severe allergies
- Connect with online communities for recipe ideas and support
Conclusion
Understanding Sesame as both a nutritious ingredient and potential allergen empowers consumers to make informed dietary choices. While Sesame provides valuable nutrients for most people, those with allergies or dietary restrictions need reliable tools to identify and avoid this ingredient. The AI Eat This app simplifies this process by providing instant, accurate ingredient analysis that works with any food product in any language.
Managing dietary restrictions doesn't have to limit your food choices or create anxiety around grocery shopping. With proper knowledge and the right technology, maintaining a Sesame-free diet becomes manageable and stress-free. Download AI Eat This for free testing today and take control of your dietary health with confidence!
70 filters
With over 70 filters, you can easily avoid certain ingredients and follow your dietary preference.

Paleo
Pescetarian

Ultra-processed food

Vegan