Everything You Need to Know About Chickpea and How AI Eat This Can Help
Chickpea, also known as garbanzo beans, is one of the most common legumes found in food products worldwide. While many people enjoy chickpea as a nutritious protein source, others need to avoid it due to allergies, intolerances, or specific dietary restrictions. Understanding where chickpea appears in processed foods can be challenging, especially when ingredient lists use technical terms or foreign languages.
The AI Eat This mobile app revolutionizes how consumers identify problematic ingredients like chickpea in their food. By simply scanning ingredient lists with your smartphone camera, this innovative tool helps you make informed dietary choices and avoid unwanted ingredients, regardless of the language on the packaging.
What Is Chickpea and Where Is It Used?
Chickpea is a versatile legume that serves multiple purposes in food manufacturing. Beyond its use as a whole food, chickpea appears in various processed forms including chickpea flour, protein isolates, and fiber additives. Food manufacturers value chickpea for its high protein content, fiber properties, and ability to improve texture in processed foods.
In the food industry, chickpea often appears under different names such as garbanzo bean, Bengal gram, or Cicer arietinum. These alternative names can make it difficult for consumers to identify chickpea in ingredient lists, particularly when dealing with dietary restrictions.
Common Foods Containing Chickpea
Chickpea appears in numerous food products, often in unexpected places. Understanding where to look for this ingredient helps consumers make better dietary choices:
- Protein bars and nutritional supplements
- Gluten-free baked goods and pasta
- Vegetarian and vegan meat alternatives
- Snack foods like chips and crackers
- Soups, stews, and ready-made meals
- Hummus and Mediterranean foods
- Baby foods and infant formulas
Is Chickpea Safe? What Does the Research Say?
For most people, chickpea is considered a safe and nutritious food ingredient. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes chickpea as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food products. Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not identified significant safety concerns with chickpea consumption for the general population.
Chickpea provides numerous nutritional benefits, including high-quality protein, dietary fiber, and essential minerals. The World Health Organization (WHO) includes legumes like chickpea in their recommendations for healthy, sustainable diets.
Regulatory Approvals and Guidelines
Health authorities worldwide have established guidelines for legume consumption, including chickpea. These organizations monitor food safety and provide recommendations based on current scientific evidence. Regular consumption of chickpea as part of a balanced diet is generally encouraged for its nutritional benefits.
Risks for Specific Groups
While chickpea is safe for most people, certain individuals may need to avoid it. People with legume allergies can experience serious reactions to chickpea, ranging from mild digestive discomfort to severe allergic responses. Additionally, some individuals may have chickpea intolerance, experiencing bloating, gas, or digestive issues after consumption.
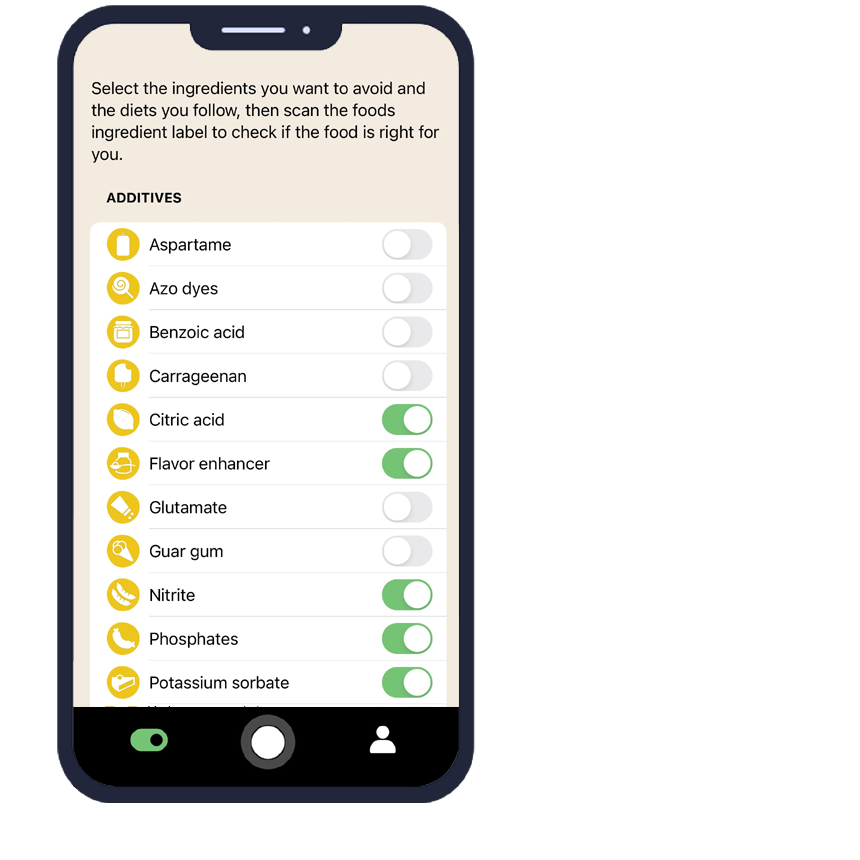
How Does AI Eat This Help You Avoid Chickpea?
The AI Eat This app transforms how consumers manage dietary restrictions by making ingredient identification simple and accurate. This powerful tool uses advanced artificial intelligence to scan and analyze ingredient lists in any language, instantly identifying chickpea and its various alternative names.
Setting up chickpea avoidance in the app is straightforward. Users can create personalized filters that automatically flag products containing chickpea, even when listed under alternative names like garbanzo bean or Bengal gram. The app's multilingual capabilities ensure you can identify problematic ingredients regardless of where you shop or travel.
The scanning feature works in real-time, providing immediate feedback about product safety. Simply point your phone's camera at an ingredient list, and the app will highlight any instances of chickpea or related compounds. This technology is particularly valuable for people with severe chickpea allergy who need to avoid even trace amounts.
Who Should Avoid Chickpea?
Several groups of people may need to limit or avoid chickpea consumption entirely. Understanding whether you fall into one of these categories helps determine if chickpea avoidance is necessary for your health and wellbeing.
Individuals with diagnosed legume allergies must strictly avoid chickpea, as exposure can trigger allergic reactions. People with chickpea intolerance may choose to limit consumption to prevent uncomfortable digestive symptoms. Some individuals following specific dietary protocols may also need to avoid legumes like chickpea.
Those with certain digestive conditions, such as SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth) or specific forms of IBS, may find that avoiding high-FODMAP foods like chickpea helps manage their symptoms. Consulting with healthcare providers helps determine the best approach for managing dietary restrictions.
Tips for a Chickpea-Free Diet
Successfully avoiding chickpea requires vigilance and planning, but the right strategies make it manageable. Reading ingredient labels carefully is essential, as chickpea can appear under various names and in unexpected products.
Focus on whole, unprocessed foods when possible, as these are less likely to contain hidden chickpea ingredients. When shopping for packaged foods, pay special attention to protein-enriched products, gluten-free items, and vegetarian alternatives, as these commonly contain legume-based ingredients.
The Mayo Clinic recommends keeping a food diary to track reactions and identify problem foods. This approach, combined with careful label reading, helps maintain a safe chickpea-free diet.
When dining out, communicate your dietary restrictions clearly to restaurant staff. Many cuisines, particularly Mediterranean and Middle Eastern foods, commonly use chickpea in various forms. Don't hesitate to ask about ingredients or preparation methods.
Conclusion
Understanding chickpea and its presence in food products is crucial for anyone managing dietary restrictions, allergies, or intolerances. While chickpea offers nutritional benefits for many people, those who need to avoid it face the challenge of identifying this ingredient in its many forms across different food products.
The AI Eat This app provides an innovative solution for managing chickpea avoidance, offering real-time ingredient scanning and personalized filtering capabilities. This technology empowers consumers to make confident food choices while maintaining their dietary restrictions.
Whether you're dealing with a chickpea allergy, intolerance, or following a specific dietary protocol, having the right tools makes all the difference. Download AI Eat This for free testing today and take control of your dietary management with confidence!
70 filters
With over 70 filters, you can easily avoid certain ingredients and follow your dietary preference.

Paleo
Pescetarian

Ultra-processed food

Vegan